Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of enterprise architecture, the importance of governance cannot be overstated. TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) recognizes this need and incorporates Architecture Governance as a vital component to align the framework with current best practices. The primary goal is to ensure an appropriate level of visibility, guidance, and control to support stakeholder requirements and obligations throughout the architectural process.
Key Information Areas in Architecture Governance
Reference Data
Reference Data plays a crucial role in providing guidance and instruction during project implementation. It serves as a compass, ensuring that the architectural decisions align with established best practices and standards.
Process Status
Managing the governance processes and the information acquired by these processes is essential. Process Status ensures that the governance mechanisms are not only in place but are actively contributing to the success of the architectural endeavors.
TOGAF Governance Approach
Conceptually, Architecture Governance is an approach, a series of processes, a cultural orientation, and set of owned responsibilities that ensure the integrity and effectiveness of the organization’s architectures. The split of process, content, and context are key to the support of the Architecture Governance initiative, by allowing the introduction of new governance material (legal, regulatory, standards-based, or legislative) without unduly impacting the processes.
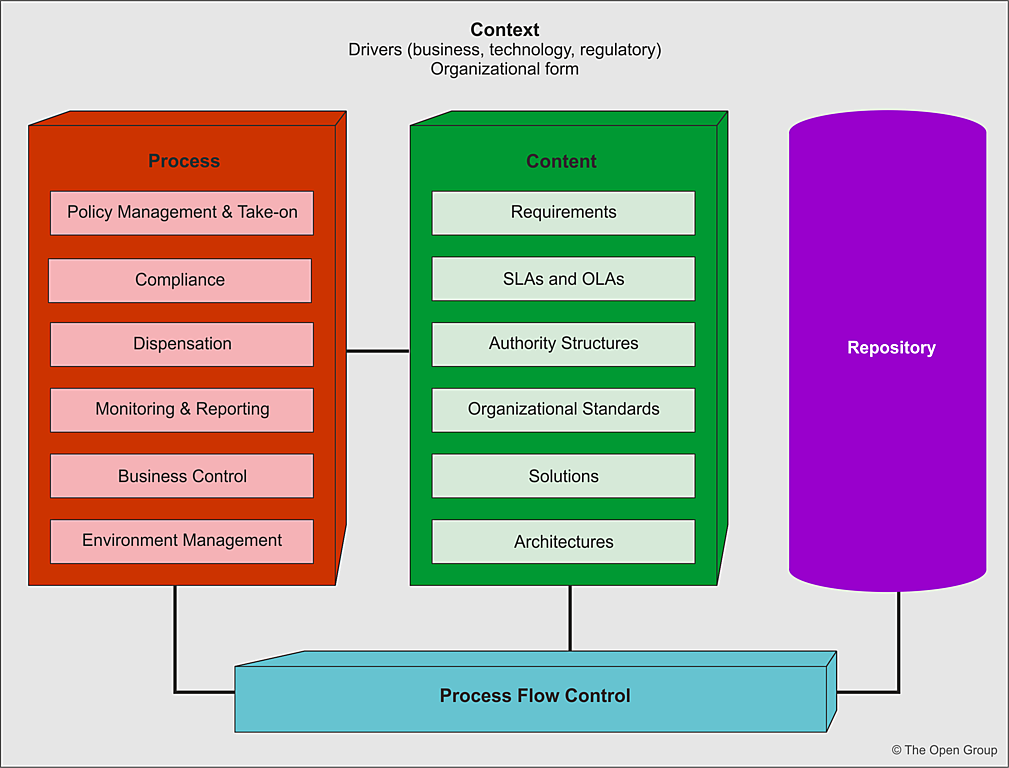
This content-agnostic approach ensures that the framework is flexible. The processes are typically independent of the content and implement a proven best practice approach to active governance. The Architecture Governance Framework is integral to the Enterprise Continuum, and manages all content relevant both to the architecture itself and to Architecture Governance processes.
Benefits of Architecture Governance
1. Increased Transparency of Accountability
Architecture Governance enhances transparency by making all activities and decision-making structures available for inspection. This transparency fosters trust and ensures that accountability is clear and understood.
2. Informed Delegation of Authority
Through clearly defined governance processes, authority can be delegated with confidence. This ensures that decision-making powers are vested in the right individuals or groups, aligning with the overall goals of the enterprise.
3. Controlled Risk Management
Effective governance provides a structured approach to risk management. By identifying, assessing, and controlling risks, architecture governance ensures that projects progress with a clear understanding of potential challenges.
4. Re-use of Processes, Concepts, and Components
Governance facilitates the re-use of successful processes, concepts, and components. This not only saves time and resources but also ensures that proven strategies contribute to the success of new architectural endeavors.
5. Value Creation through Monitoring and Evaluation
Architecture Governance creates value by actively monitoring, measuring, evaluating, and providing feedback on processes and decisions. This continuous improvement loop ensures that the architecture aligns with evolving business needs.
6. Increased Visibility of Decisions at All Levels
Through well-defined governance structures, decisions become visible at all levels of the enterprise. This visibility fosters collaboration and ensures that decisions align with the broader strategic objectives.
7. Increased Shareholder Value
Architecture Governance directly contributes to increasing shareholder value by ensuring that architectural decisions align with business objectives and deliver tangible benefits.
8. Integration with Existing Solutions
By providing control capabilities, architecture governance seamlessly integrates with existing solutions, ensuring that the architectural framework works harmoniously with other governance structures like corporate governance, technology governance, and IT governance.
Audit Information
Audit Information serves as a recorded history of process actions, supporting key decisions, identifying responsible personnel, and providing a reference for future process developments. It establishes a foundation for learning from past experiences and improving governance practices.
Implementation of Architecture Governance
Architecture Governance is positioned as a distinct domain within a hierarchy of governance structures. It complements and interacts with other governance layers, including:
- Corporate Governance
- Technology Governance
- IT Governance
The success of architecture governance lies in specific characteristics that amplify its value and necessity in an enterprise:
1. Discipline
There is a commitment to adhering to procedures, processes, and authority structures. This discipline ensures consistency and predictability in architectural decision-making.
2. Transparency
All activities and decision-making structures are available for inspection, promoting openness and trust within the organization.
3. Independence
Processes, decision-making, and mechanisms are established to minimize and avoid potential conflicts of interest. Independence ensures that decisions are made with the best interests of the enterprise in mind.
4. Accountability
Groups are authorized and accountable for their actions. This ensures that decisions have ownership and responsibility attached to them.
5. Responsibility
Contracted parties are required to act responsibly. This responsibility extends to all stakeholders involved in the architectural process.
6. Fairness
Activities and solutions do not create an unfair advantage for a particular party. Fairness is crucial to maintaining a level playing field and ensuring equitable outcomes.
Conclusion
Architecture Governance in TOGAF is a multifaceted approach that not only aligns the architectural framework with best practices but also ensures that the decision-making processes are transparent, accountable, and contribute to the overall success of the enterprise. It is a critical element in navigating the complex landscape of enterprise architecture, providing the necessary guidance and control for sustainable and effective architectural outcomes.