Introduction
The TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) ADM (Architecture Development Method) provides a robust framework for developing enterprise architecture. At its core lies the metamodel, a structured representation of essential entities and relationships that form the foundation of architectural content. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the Core Metamodel, unraveling its key entities and their relationships.
Understanding the Core Metamodel:
The Core Metamodel in TOGAF ADM serves as the backbone for architectural development, offering a minimal set of entities to ensure traceability across artifacts. It comprises key entities that represent various aspects of the enterprise architecture. Let’s delve into these entities:
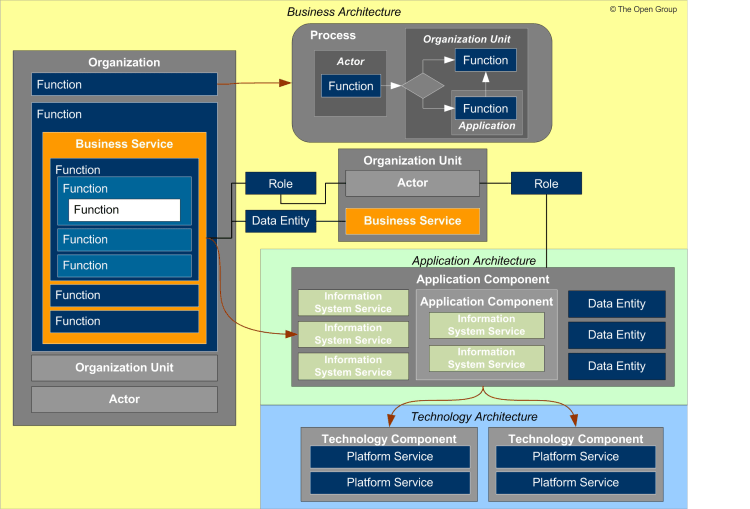
Actor:
- Definition: A person, organization, or system external to the architecture model that interacts with it.
- Role: Actors assume roles to perform specific tasks.
Application Component:
- Definition: An encapsulation of application functionality aligned to implementation structuring.
- Role: Application components are fundamental units supporting the implementation of business capabilities.
Business Service:
- Definition: Supports business capabilities through a defined interface, governed by the organization.
- Role: Business services act as boundaries for one or more functions, operating at a granularity consistent with governance needs.
Data Entity:
- Definition: An encapsulation of data recognized by business domain experts.
- Role: Data entities can be tied to applications, repositories, and services, structured based on implementation considerations.
Function:
- Definition: Delivers business capabilities closely aligned to an organization.
- Role: Functions represent units of business capability at all levels of granularity.
Information System Service:
- Definition: Automated elements of a business service, delivering or supporting part or all of one or more business services.
- Role: Information system services bridge the gap between business services and technical implementation.
Organization Unit:
- Definition: A self-contained unit of resources with goals, objectives, and measures.
- Role: Organization units encompass internal and external parties, forming self-contained entities.
Platform Service:
- Definition: Technical capability required to provide enabling infrastructure supporting application delivery.
- Role: Platform services contribute to the technical backbone that facilitates application deployment.
Role:
- Definition: An actor assumes a role to perform a task.
- Role: Roles define the specific tasks an actor can undertake within the architecture.
Technology Component:
- Definition: An encapsulation of technology infrastructure representing a class or specific technology product.
- Role: Technology components form the technological building blocks supporting the overall architecture.
Relationship Concepts:
Understanding the relationships between these entities is crucial for effective architectural development. Some key relationship concepts include:
Process and Flow:
- Use processes to describe the flow of interactions between functions and services.
- Processes cannot be physically deployed but are executed through the functions they support.
Function Granularity:
- “Function” describes units of business capability at all levels of granularity.
- Encapsulates terms like value chain, process area, capability, and business function.
Business Services Deployment:
- Business services support organizational objectives and are defined at a governance-appropriate granularity.
- Deployed onto application components, forming a crucial link between business and technology.
Conclusion
The TOGAF ADM Core Metamodel provides a structured foundation for enterprise architecture development. By understanding the entities and their relationships, architects can navigate the complexity of organizational structures, technological components, and business processes. As organizations tailor these concepts to meet their specific needs, the Core Metamodel proves to be a versatile and powerful tool in the realm of enterprise architecture.