1. Introduction to Migration Planning
Migration planning is a critical component of the TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM). It involves the systematic approach to transitioning from the current architecture (baseline) to the target architecture. Effective migration planning ensures that the transition is smooth, minimizes risks, and aligns with the organization’s strategic goals.
2. Key Concepts and Principles
2.1 Baseline and Target Architectures
- Baseline Architecture: The current state of the enterprise architecture.
- Target Architecture: The desired future state of the enterprise architecture.
2.2 Transition Architectures
- Transition Architectures: Intermediate states between the baseline and target architectures that facilitate a phased migration approach.
2.3 Migration Strategy
- Migration Strategy: The overall approach and plan for migrating from the baseline to the target architecture, including the sequence of transitions and the methods used.
3. Migration Planning Techniques
3.1 Implementation Factor Catalog
The Implementation Factor Catalog is a technique used to document factors impacting the architecture Implementation and Migration Plan. The catalog includes a list of factors, their descriptions, and the deductions that indicate the actions or constraints to be considered when formulating the plans.
Factors to Consider:
- Risks
- Issues
- Assumptions
- Dependencies
- Actions
- Impacts
Example:
| Implementation Factor Catalog | ||
|---|---|---|
| Factor | Description | Deduction |
| Change in Technology | Shut down the message centers, saving 700 personnel, and have them replaced by email. | – Need for personnel training, re-assignment – Email has major personnel savings and should be given priority |
| Consolidation of Services | ||
| Introduction of New Customer Service |
3.2 Consolidated Gaps, Solutions, and Dependencies Matrix
The Consolidated Gaps, Solutions, and Dependencies Matrix allows architects to group the gaps identified in the domain architecture gap analysis results and assess potential solutions and dependencies to one or more gaps. This matrix serves as a planning tool when creating work packages and drives the creation of projects and migration planning in Phases E and F.
Example:
| Consolidated Gaps, Solutions, and Dependencies Matrix | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Architecture | Gap | Potential Solutions | Dependencies |
| 1 | Business | New Order Processing Process | Use COTS software tool process Implement custom solution | Drives applications (2) |
| 2 | Application | New Order Processing Application | COTS software tool X Develop in-house | |
| 3 | Information | Consolidated Customer Information Base | Use COTS customer base Develop customer data mart |
3.3 Architecture Definition Increments Table
The Architecture Definition Increments Table allows architects to plan a series of Transition Architectures outlining the status of the Enterprise Architecture at specified times. The table lists the projects and assigns their incremental deliverables across the Transition Architectures.
Example:
| Architecture Definition · Project Objectives by Increment (Example Only) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project | April 2015/2019 | April 2015/2020 | April 2020/2021 | |
| Transition Architecture 1: Preparation | Transition Architecture 2: Initial Operational Capability | Transition Architecture 3: Benefits | Comments | |
| Enterprise e-Services Capability | Training and Business Process | e-Licensing Capability | e-Employment Benefits | |
| IT e-Forms | Design and Build | |||
| IT e-Information Environment | Design and Build Information Environment | Client Common Data Web Content Design and Build | Enterprise Common Data Component Management Design and Build |
3.4 Transition Architecture State Evolution Table
The Transition Architecture State Evolution Table allows architects to show the proposed state of the architectures at various levels using the defined taxonomy (e.g., the TOGAF TRM). The table lists the services from the taxonomy used in the enterprise, the Transition Architectures, and proposed transformations.
Example:
| Architectural State using the Technical Reference Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-Domain | Service | Transition Architecture 1 | Transition Architecture 2 | Transition Architecture 3 |
| Infrastructure Applications | Information Exchange Services | Solution System A (replace) | Solution System B-1 (transition) | Solution System B-2 (new) |
| Data Management Services | Solution System D (retain) | Solution System D (retain) | Solution System D (retain) |
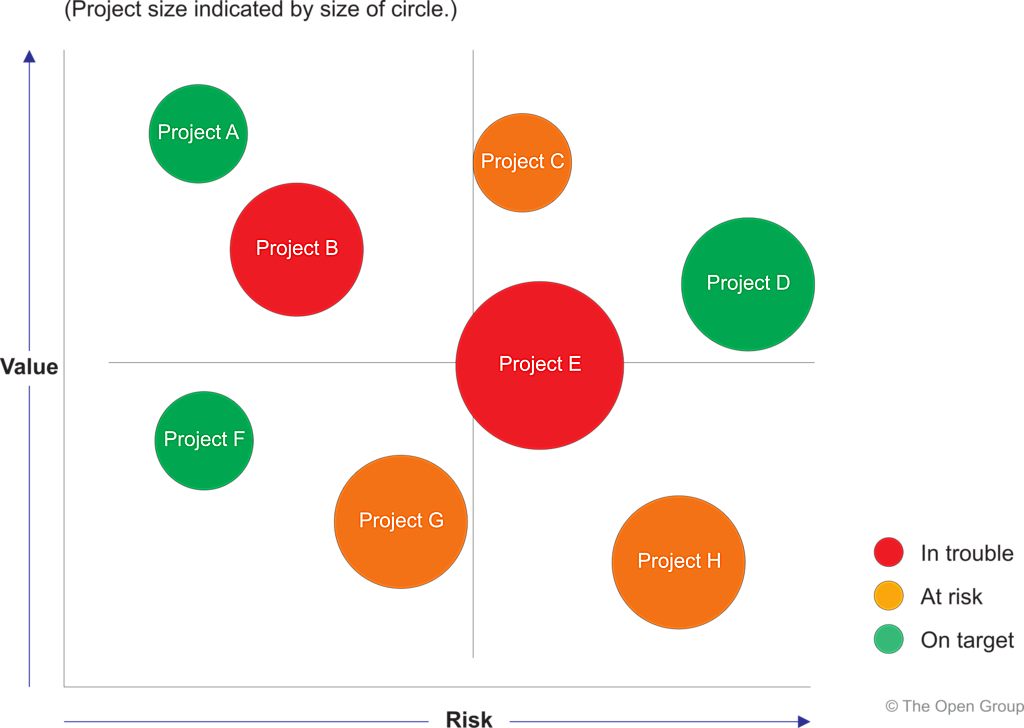
3.5 Business Value Assessment Technique
The Business Value Assessment Technique involves creating a matrix based on a value index dimension and a risk index dimension. The value index includes criteria such as compliance to principles, financial contribution, strategic alignment, and competitive position. The risk index includes criteria such as size and complexity, technology, organizational capacity, and impact of a failure. Each criterion is assigned an individual weight.
Example:
4. Steps in Migration Planning
4.1 Assess the Current State
- Activities: Document the baseline architecture, identify current issues and constraints.
- Tools: Architecture repository, current state analysis tools.
4.2 Define the Target State
- Activities: Develop the target architecture, align it with business goals and strategies.
- Tools: TOGAF ADM, architecture modeling tools.
4.3 Develop Transition Architectures
- Activities: Create intermediate architectures that bridge the gap between the baseline and target architectures.
- Tools: Transition planning tools, roadmap development tools.
4.4 Create a Migration Strategy
- Activities: Define the migration approach, sequence of transitions, and methods.
- Tools: Strategy development tools, risk assessment tools.
4.5 Plan the Migration
- Activities: Develop detailed migration plans, including timelines, resources, and milestones.
- Tools: Project management tools, Gantt charts.
4.6 Execute the Migration
- Activities: Implement the migration plan, monitor progress, and manage risks.
- Tools: Change management tools, monitoring and reporting tools.
4.7 Review and Optimize
- Activities: Evaluate the migration outcomes, identify lessons learned, and optimize future migrations.
- Tools: Post-implementation review tools, continuous improvement frameworks.
5. Tools and Resources
5.1 Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF ADM Guide-Through Process
- Description: Provides step-by-step instructions, input references, and real-world samples to streamline the EA process and kick-start projects of any size.
- Features: Instructions, samples, steps, input references for performing analysis.
5.2 Powerful TOGAF ADM Toolset
- Description: Simplifies navigating and developing deliverables using standard TOGAF ADM diagrams, reducing the need for extensive documentation and references.
- Features: Step-by-step process tool, deliverable composer, easy-to-follow instructions.
5.3 TOGAF Guide-Through Process
- Description: Automated guide-through process with step-by-step instructions, input references, and samples to develop deliverables incrementally and collaboratively.
- Features: Instructions, input references, samples, collaborative development.
6. Best Practices
6.1 Stakeholder Engagement
- Practice: Engage stakeholders from various domains (project owners, business analysts, enterprise architects, and IT professionals) to ensure collaboration and alignment.
- Benefits: Enhances communication, ensures buy-in, and addresses diverse perspectives.
6.2 Risk Management
- Practice: Identify and mitigate risks associated with the migration, including technical, operational, and cultural risks.
- Benefits: Reduces potential disruptions, ensures smooth transition.
6.3 Continuous Improvement
- Practice: Regularly review and optimize the migration process based on feedback and lessons learned.
- Benefits: Enhances the effectiveness of future migrations, promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
7. Case Studies and Examples
7.1 Enterprise-Wide ERP Implementation
- Context: A large manufacturing company implementing a new ERP system.
- Approach: Phased implementation starting with core modules (finance, procurement) followed by advanced modules (supply chain, CRM).
- Outcome: Successful migration with minimal disruption, incremental benefits realization.
7.2 Cloud Migration for a Financial Services Firm
- Context: A financial services firm migrating its data center to the cloud.
- Approach: Pilot project in a single business unit, followed by parallel running of old and new systems, and finally a big bang cutover.
- Outcome: Seamless transition, improved scalability and cost efficiency.
8. Conclusion
Migration planning in TOGAF ADM is a structured approach to transitioning from the current to the target architecture. By leveraging techniques such as the Implementation Factor Catalog, Consolidated Gaps, Solutions, and Dependencies Matrix, Architecture Definition Increments Table, Transition Architecture State Evolution Table, and Business Value Assessment Technique, organizations can effectively manage the migration process. Tools like Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF ADM Guide-Through Process and best practices in stakeholder engagement, risk management, and continuous improvement ensure a successful migration. Case studies and real-world examples illustrate the practical application of these techniques, providing valuable insights for enterprise architects.
TOGAF ADM Resources
- Working with TOGAF ADM Guide-through
- This article provides an overview of Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF ADM Guide-Through Process, which is designed to streamline the entire enterprise architecture (EA) process. It includes features such as instructions, samples, steps, and input references for performing analysis11.
- Unlock the Power of TOGAF® with Visual Paradigm’s ADM Guide-Through Process
- This guide discusses how Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF ADM Guide-Through Process can help both new and experienced enterprise architects kick-start projects of any size. It emphasizes the step-by-step instructions, input references, and real-world samples provided by the process12.
- Powerful TOGAF ADM Toolset
- This article highlights Visual Paradigm’s innovative TOGAF tool, which simplifies the process of navigating and developing deliverables using standard TOGAF ADM diagrams. It emphasizes the tool’s ability to streamline the architecture development process and reduce the need for extensive documentation and references13.
- Visual Paradigm TOGAF – Everything about TOGAF, Enterprise Architecture, ArchiMate, and more
- This resource delves into the nuanced strategy required to market the Implementation and Migration Plan proposed by TOGAF. It emphasizes the careful orchestration of communication, human resource considerations, and cultural nuances within the TOGAF ADM14.
- Step-by-Step Enterprise Architecture Tutorial with TOGAF
- This tutorial provides a step-by-step guide to developing enterprise architecture using TOGAF ADM. It includes detailed instructions on how to perform activities required in each phase of the ADM cycle15.
- TOGAF ADM Guide-Through
- This chapter provides an overview of TOGAF ADM, its development, and its adoption by major companies. It explains how TOGAF ADM integrates various architectural elements to meet business and IT needs16.
- Unlock the Power of TOGAF ADM with Visual Paradigm’s Guide-Through Process
- This article discusses how Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF ADM Process Navigator can help steer projects toward success by providing a streamlined process that guides users through every step of the architecture development process17.
- TOGAF Guide-Through Process
- This resource explains how Visual Paradigm’s automated TOGAF ADM guide-through process helps kick-start projects of any size. It includes step-by-step instructions, input references, and samples to develop deliverables incrementally and collaboratively18.
- TOGAF ADM and Architecture Content Framework
- This article provides an overview of the TOGAF ADM and the Architecture Content Framework. It explains how the content framework provides a structural model for architectural content and how it can be used to map TOGAF content to other frameworks19.
- A Practical Tutorial for TOGAF
- This tutorial explains how the ADM describes the process of deriving an organization-specific enterprise architecture that addresses business requirements. It provides guidelines and techniques for applying the ADM and discusses the iterative nature of the ADM process20.