Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of modern enterprises, the effective management of architecture is paramount for achieving strategic objectives, optimizing operations, and ensuring long-term success. The TOGAF 9 Architecture Capability Framework serves as a guiding beacon for organizations seeking to establish and maintain a robust enterprise architecture capability. This framework, encapsulated in Table 6, outlines key chapters that provide comprehensive guidelines and reference materials. In this exploration, we delve into the essence of these chapters, shedding light on how they collectively contribute to the seamless integration of enterprise architecture practices within an organization.
Establishing and maintaining an enterprise architecture capability in TOGAF involves leveraging the Architecture Capability Framework, as outlined in Table 6. Let’s break down the key chapters and their respective descriptions:
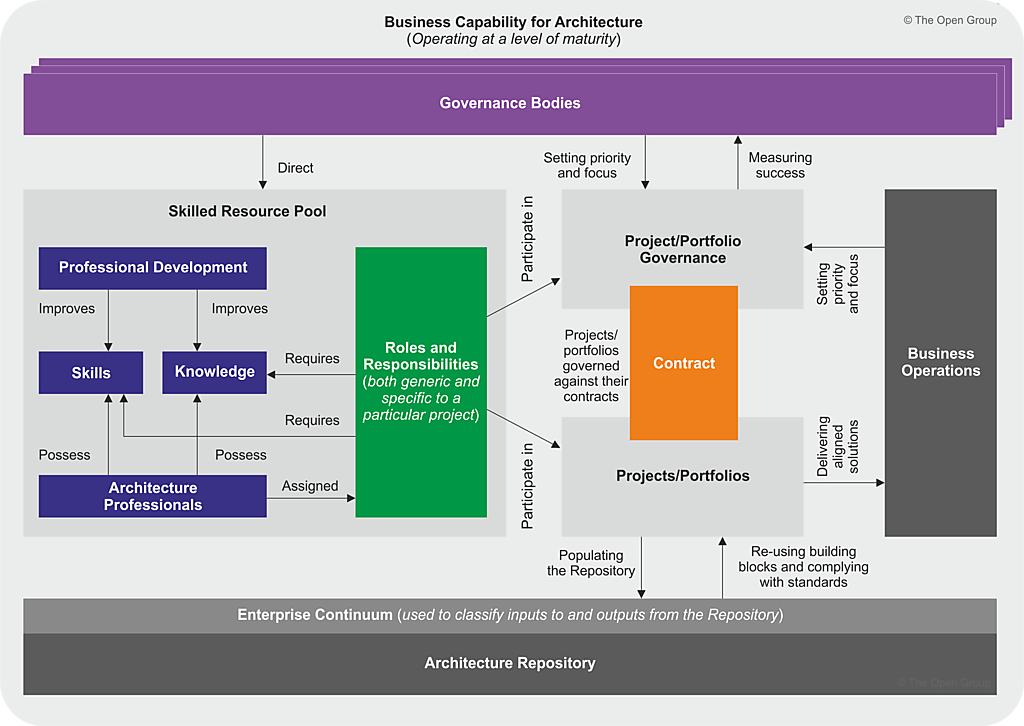
Establishing an Architecture Capability:
This chapter provides guidelines for setting up an architecture capability within an organization. It involves defining the structure, roles, responsibilities, and processes necessary for effective enterprise architecture.
Architecture Board:
Guidelines are offered for establishing and operating an enterprise Architecture Board. This board is crucial for overseeing and making decisions related to architectural issues, ensuring alignment with business objectives.
Architecture Compliance:
This section provides guidelines to ensure that projects adhere to the defined architecture. It involves mechanisms for validating and enforcing compliance with established architectural standards and principles.
Architecture Contracts:
Guidelines for defining and utilizing Architecture Contracts are presented. These contracts serve as agreements between different stakeholders, outlining their roles and responsibilities in the context of enterprise architecture.
Architecture Governance:
This chapter introduces a framework and guidelines for Architecture Governance. Governance ensures that the enterprise architecture aligns with organizational goals, standards, and policies. It involves decision-making processes and mechanisms for enforcing compliance.
Architecture Maturity Models:
Techniques are provided for evaluating and quantifying an organization’s maturity in enterprise architecture. This involves assessing the organization’s capabilities, processes, and the effectiveness of its architecture function over time.
Architecture Skills Framework:
This section defines a set of norms for the roles, skills, and experiences required for staff engaged in enterprise architecture work. It helps in identifying and developing the skills necessary for effective architectural practice within the organization.
By leveraging these chapters, organizations can systematically establish, operate, and enhance their enterprise architecture capability according to TOGAF guidelines. This framework provides a structured approach to ensure that architectural practices align with business objectives and contribute to overall organizational success.
Summary
The Architecture Capability Framework within TOGAF 9 is a holistic guide designed to empower organizations in their journey towards establishing and sustaining a resilient enterprise architecture capability. From the foundational aspects of setting up an architecture capability to the intricacies of governance, compliance, and skills development, each chapter plays a pivotal role. Whether it’s the establishment of an Architecture Board, ensuring project compliance, defining and utilizing Architecture Contracts, or evaluating organizational maturity through Maturity Models, TOGAF provides a structured approach. The Architecture Skills Framework adds the human element, delineating the roles, skills, and experiences necessary for success in enterprise architecture endeavors. By embracing these guidelines, organizations can foster agility, alignment, and innovation through a well-crafted and diligently maintained enterprise architecture capability.